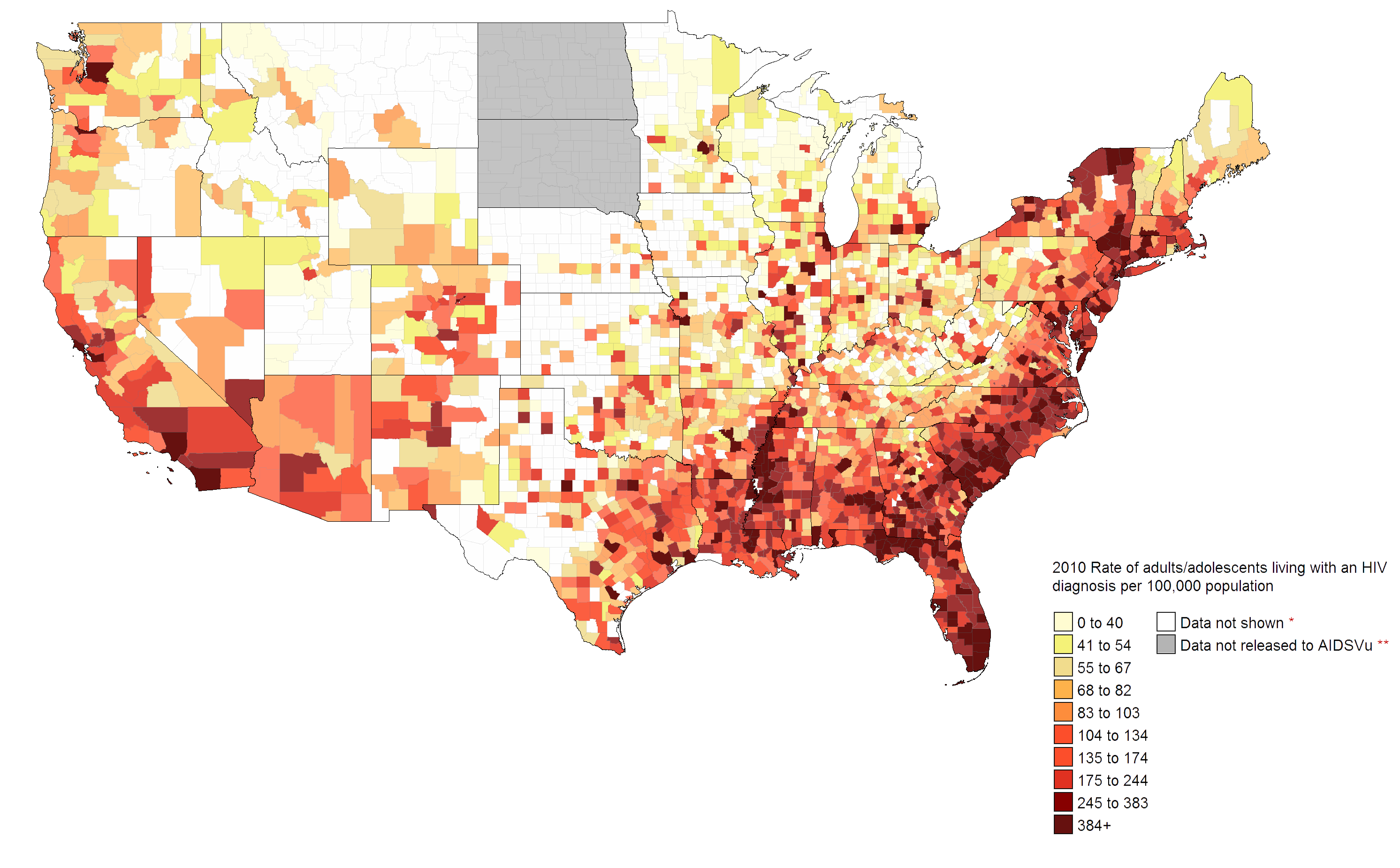
Low socioeconomic status heterosexuals in major U.S. urban areas often engage in sex that puts them at risk for HIV, but do not get tested at high enough rates. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued its most recent National HIV Behavior Surveillance System (NHBS) report about high-risk heterosexuals, which focuses on data collected from individuals in a series of major metropolitan areas.
In 2010, investigators conducted a behavior survey among 9,278 heterosexuals who reported vaginal or anal sex with at least one opposite-sex partner during the previous 12 months, did not report injection drug use, and, among the men, who did not report recent sex with other men. The participants had an income at or below the poverty level or had only a high school education.
The median age of the participants was 35. Forty-seven percent were men. Seventy-two percent were African American and 21 percent were Latino.
Eighty-eight percent of the men and 90 percent of the women reported having condomless vaginal sex with one or more opposite-sex partners during the previous 12 months. Thirty percent of the men and 29 percent of the women reported condomless anal sex.
Fifty-nine percent of the participants reported using noninjection drugs during the previous year, with 15 percent reporting using crack cocaine.
Seventy-one percent of the men and 77 percent of the women had been tested for HIV previously. Among Latinos, just 52 percent of the men and 62 percent of the women had been tested.